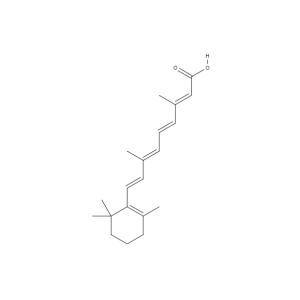
All-Trans Retinoic Acid
Catalog Number : 3027949
description
Retinoic Acid is vitamin A derivative that is an agonist for the retinoic acid receptors, which act as transcription factors that regulate the growth and differentiation of normal and malignant cells. It is reported to promote the differentiation of embryonic cells into motor neurons, pancreatic progenitors and cardiomyocytes.
Additional Information
|
Applications:
|
FA
|
|
Synonyms:
|
NSC 122578, Vitamin A Acid, Tretinoin, ATRA
|
|
Formulation:
|
Crystalline solid
|
|
Chemical Name:
|
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid
|
|
Molecular Formula:
|
C20H28O2 |
|
Molecular Weight: |
300.4
|
|
CAS Number
|
302-79-4
|
|
Purity:
|
≥98%
|
|
Storage Conditions:
|
Product should be kept at -20°C.
|
|
References:
|
Dani, C., Smith, A. G., Dessolin, S., Leroy, P., Staccini, L., Villageois, P., ... & Ailhaud, G. (1997). Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into adipocytes in vitro. Journal of cell science, 110(11), 1279-1285. Wobus, A. M., Kaomei, G., Shan, J., Wellner, M. C., Rohwedel, J., Guanju, J., ... & Franz, W. M. (1997). Retinoic acid accelerates embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac differentiation and enhances development of ventricular cardiomyocytes. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 29(6), 1525-1539. Takahashi, J., Palmer, T. D., & Gage, F. H. (1999). Retinoic acid and neurotrophins collaborate to regulate neurogenesis in adult‐derived neural stem cell cultures. Journal of neurobiology, 38(1), 65-81. |